Abstract
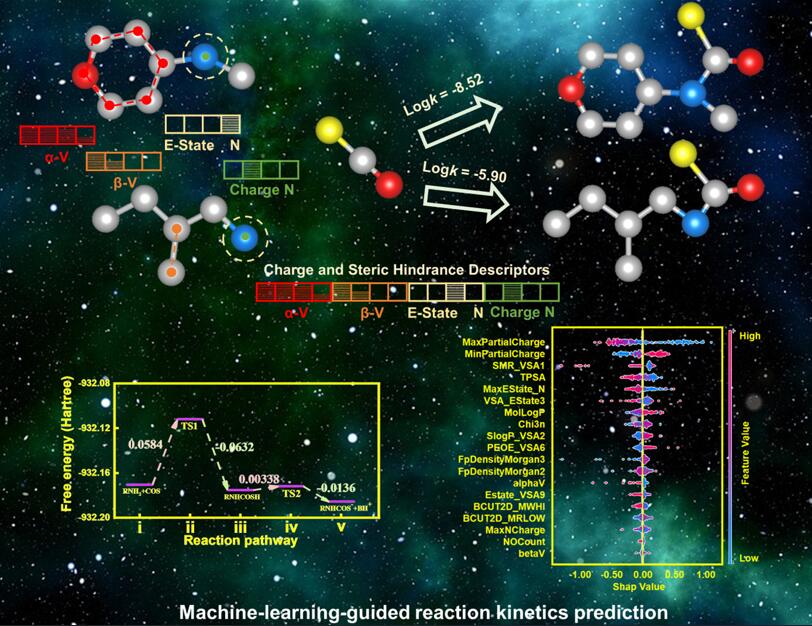
Exploring solvents for chemical absorption of carbonyl sulfide (COS) is largely hindered because of challenging study of reaction kinetics by means of either experimental or computational methods. Machine learning (ML) has been proven to greatly accelerate information identification and function achievement in academic and industrial fields. Herein, we report a machine-learning-guided reaction kinetics prediction for intelligent identification of promising compounds for chemical absorption of COS. The rate-determining step for solvent-involved reaction of COS was firstly recognized and the reaction rate constants of determining step were obtained via quantum chemistry computations in order to establish the initial training dataset. Furthermore, two molecular descriptors, alphaV and betaV, representing the steric hindrance around the amine groups were defined to build the ML algorithm and the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) approach was used to interpret the model. By introducing four specific descriptors, our ML model exhibits the largely reduced mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.80 for predicting the rate constants (logk) for COS reaction with potential solvents. These reaction rates are primarily determined by the charge distribution and steric hindrance of solvent molecules. Documented data confirm that our ML model involving custom-defined molecular descriptors successfully predict the reaction kinetics. This study enables a general strategy for machine-learning-guided exploration and identification of solvent candidates for compound capture and separation through chemical absorption process.